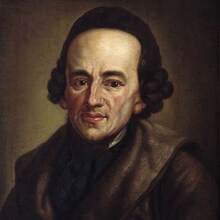Klaus Nomi
1944 - 1983
New wave synthpop opera experimental baroque
Klaus Nomi
1944 - 1983
New wave synthpop opera experimental baroque
 Erich Alfred Hartmann
1922 - 1993
Fighter pilot, flying ace, military officer
Erich Alfred Hartmann
1922 - 1993
Fighter pilot, flying ace, military officer
 Frederick William I of Prussia
1688 - 1740
King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg
Frederick William I of Prussia
1688 - 1740
King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg
 Walter Gropius
1883 - 1969
Founder of the Bauhaus School
Walter Gropius
1883 - 1969
Founder of the Bauhaus School
 Albrecht Altdorfer
1480 - 1538
Renaissance painter, landscape artist, printmaker
Albrecht Altdorfer
1480 - 1538
Renaissance painter, landscape artist, printmaker
 Bertolt Brecht
1898 - 1956
playwright
Bertolt Brecht
1898 - 1956
playwright
 Albert Einstein
1879 - 1955
Theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate
Albert Einstein
1879 - 1955
Theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate
 Kurt Julian Weill
1900 - 1950
Composer for the stage and concert hall
Kurt Julian Weill
1900 - 1950
Composer for the stage and concert hall
 Moses Mendelssohn
1729 - 1786
Philosopher and theologian
Moses Mendelssohn
1729 - 1786
Philosopher and theologian
 Hans Oster
1887 - 1945
Deputy head of the Abwehr
Hans Oster
1887 - 1945
Deputy head of the Abwehr
 Frank Herbert Dedrick Pickersgill
1915 - 1944
SOE Agent
Frank Herbert Dedrick Pickersgill
1915 - 1944
SOE Agent
 Erik Homburger Erikson
1902 - 1994
Psychosocial development theory
Erik Homburger Erikson
1902 - 1994
Psychosocial development theory
 Ferdinand von Zeppelin
1838 - 1917
Inventor of rigid airships
Ferdinand von Zeppelin
1838 - 1917
Inventor of rigid airships
 Willem Frederik
1772 - 1843
the first King of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
Willem Frederik
1772 - 1843
the first King of the Kingdom of the Netherlands
 Princess Feodora of Leiningen
1802 - 1872
Queen Victoria's half-sister
Princess Feodora of Leiningen
1802 - 1872
Queen Victoria's half-sister
 Sigurd Ibsen
1859 - 1930
Prime minister of Norway in Stockholm
Sigurd Ibsen
1859 - 1930
Prime minister of Norway in Stockholm
 Rupprecht Maria Luitpold Ferdinand
1869 - 1955
Heir to the Bavarian throne
Rupprecht Maria Luitpold Ferdinand
1869 - 1955
Heir to the Bavarian throne
 Oswald Spengler
1880 - 1936
Author of The Decline of the West
Oswald Spengler
1880 - 1936
Author of The Decline of the West
 Edith Frank
1900 - 1945
Mother of Anne and Margot Frank
Edith Frank
1900 - 1945
Mother of Anne and Margot Frank
 Louise Mountbatten
1889 - 1965
Queen consort of Sweden, nurse in the Red Cross
Louise Mountbatten
1889 - 1965
Queen consort of Sweden, nurse in the Red Cross
 Samuel Hahnemann
1755 - 1843
Founder of homeopathy
Samuel Hahnemann
1755 - 1843
Founder of homeopathy
 Hans Holbein the Younger
1497 - 1543
Portraitist and printmaker
Hans Holbein the Younger
1497 - 1543
Portraitist and printmaker
 Ernest Louis, Grand Duke of Hesse
1868 - 1937
Grand Duke of Hesse and by Rhine
Ernest Louis, Grand Duke of Hesse
1868 - 1937
Grand Duke of Hesse and by Rhine
 Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
 Ludwig Feuerbach
1804 - 1872
Philosopher and anthropologist
Ludwig Feuerbach
1804 - 1872
Philosopher and anthropologist
 Oskar Schindler
1908 - 1974
Saving 1,200 Jews during the Holocaust
Oskar Schindler
1908 - 1974
Saving 1,200 Jews during the Holocaust
 Jakob Savinsek
1922 - 1961
Sculptor
Jakob Savinsek
1922 - 1961
Sculptor
 Princess Marie-Auguste of Anhalt
1898 - 1983
Princess of Prussia
Princess Marie-Auguste of Anhalt
1898 - 1983
Princess of Prussia
 Max Schreck
1879 - 1936
Actor, best known for his role as Count Orlok
Max Schreck
1879 - 1936
Actor, best known for his role as Count Orlok
 Georg Philipp Friedrich Freiherr von Hardenberg
1772 - 1801
Romantic poet and philosopher
Georg Philipp Friedrich Freiherr von Hardenberg
1772 - 1801
Romantic poet and philosopher
 Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau
1888 - 1931
Film director, producer, screenwriter
Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau
1888 - 1931
Film director, producer, screenwriter
 Katharina von Bora
1499 - 1552
Reformer's wife
Katharina von Bora
1499 - 1552
Reformer's wife
 Theodor Schwann
1810 - 1882
Physiologist and founder of modern histology
Theodor Schwann
1810 - 1882
Physiologist and founder of modern histology
 Sophie Scholl
1921 - 1943
Anti-Nazi political activist
Sophie Scholl
1921 - 1943
Anti-Nazi political activist
 Charles Bukowski
1920 - 1994
Poet, novelist, short story writer, columnist
Charles Bukowski
1920 - 1994
Poet, novelist, short story writer, columnist
 Hermann Ebbinghaus
1850 - 1909
Experimental study of memory
Hermann Ebbinghaus
1850 - 1909
Experimental study of memory
 Max Born
1882 - 1970
Quantum mechanics pioneer
Max Born
1882 - 1970
Quantum mechanics pioneer
 Heinrich Heine
1797 - 1856
Poet, writer and literary critic
Heinrich Heine
1797 - 1856
Poet, writer and literary critic
 Friedrich Fromm
1888 - 1945
Commander in Chief of the Replacement Army
Friedrich Fromm
1888 - 1945
Commander in Chief of the Replacement Army
 Primoz Trubar
1508 - 1586
Protestant Reformer
Primoz Trubar
1508 - 1586
Protestant Reformer
 Friedrich Ebert
1871 - 1925
Leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany
Friedrich Ebert
1871 - 1925
Leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany
 Herbert Marcuse
1898 - 1979
Political philosopher and social theorist
Herbert Marcuse
1898 - 1979
Political philosopher and social theorist
 Gertrude the Great
1256 - 1302
Benedictine nun and mystic writer
Gertrude the Great
1256 - 1302
Benedictine nun and mystic writer
 Ralph Henry Baer
1922 - 2014
Inventor of the first home video game console
Ralph Henry Baer
1922 - 2014
Inventor of the first home video game console
 Louis Ferdinand, Prince of Prussia
1772 - 1806
Soldier and musician
Louis Ferdinand, Prince of Prussia
1772 - 1806
Soldier and musician
 Erich Maria Remarque
1898 - 1970
Writer and novelist
Erich Maria Remarque
1898 - 1970
Writer and novelist
 Albert Bierstadt
1830 - 1902
Landscape painter of the American West
Albert Bierstadt
1830 - 1902
Landscape painter of the American West
 Magda Goebbels
1901 - 1945
Wife of Nazi propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels
Magda Goebbels
1901 - 1945
Wife of Nazi propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels
 Johannes Kepler
1571 - 1630
Astronomer and mathematician
Johannes Kepler
1571 - 1630
Astronomer and mathematician
 Yevgeny Primakov
1929 - 2015
Prime Minister of Russia
Yevgeny Primakov
1929 - 2015
Prime Minister of Russia
 Werner Karl Heisenberg
1901 - 1976
Theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate
Werner Karl Heisenberg
1901 - 1976
Theoretical physicist and Nobel laureate
 Otto von Bismarck
1815 - 1898
Chancellor of Germany, unifier of Germany
Otto von Bismarck
1815 - 1898
Chancellor of Germany, unifier of Germany
 Ovid Samuel Crohmalnicean
1921 - 2000
Literary Critic
Ovid Samuel Crohmalnicean
1921 - 2000
Literary Critic
 Victoria Adelaide Mary Louisa
1840 - 1901
German Empress and Queen of Prussia
Victoria Adelaide Mary Louisa
1840 - 1901
German Empress and Queen of Prussia
 Bert Kaempfert
1923 - 1980
Orchestra leader, music producer
Bert Kaempfert
1923 - 1980
Orchestra leader, music producer
 Michael Klein
1959 - 1993
Footballer
Michael Klein
1959 - 1993
Footballer
 Nathan Mayer Rothschild
1777 - 1836
Founder of the English branch
Nathan Mayer Rothschild
1777 - 1836
Founder of the English branch
 Stefan Askenase
1896 - 1985
Classical pianist and pedagogue
Stefan Askenase
1896 - 1985
Classical pianist and pedagogue
 Gretl Braun
1915 - 1987
Sister of Eva Braun
Gretl Braun
1915 - 1987
Sister of Eva Braun
 Gunther Behnisch
1922 - 2010
Architect of Olympic Park in Munich
Gunther Behnisch
1922 - 2010
Architect of Olympic Park in Munich
 Willy Brandt
1913 - 1992
Chancellor of West Germany
Willy Brandt
1913 - 1992
Chancellor of West Germany
 Alois Alzheimer
1864 - 1915
Identifying Alzheimer's disease
Alois Alzheimer
1864 - 1915
Identifying Alzheimer's disease
 Helmut Newton
1920 - 2004
Fashion photographer
Helmut Newton
1920 - 2004
Fashion photographer
 Carl Philipp Gottfried von Clausewitz
1780 - 1831
Prussian general and military strategist
Carl Philipp Gottfried von Clausewitz
1780 - 1831
Prussian general and military strategist
 Georg Philipp Telemann
1681 - 1767
Baroque composer and multi-instrumentalist
Georg Philipp Telemann
1681 - 1767
Baroque composer and multi-instrumentalist
 Elisabeth Bohm
1921 - 2012
Architect
Elisabeth Bohm
1921 - 2012
Architect
 Ossy Chinedu Prestige
1965 - 2021
Businessman and legislator
Ossy Chinedu Prestige
1965 - 2021
Businessman and legislator
 Heinrich Boll
1917 - 1985
Writer and Nobel laureate
Heinrich Boll
1917 - 1985
Writer and Nobel laureate
 Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate
1652 - 1722
Correspondent and memoirist
Elizabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate
1652 - 1722
Correspondent and memoirist
 Karl Friedrich Benz
1844 - 1929
Automobile engineer and inventor
Karl Friedrich Benz
1844 - 1929
Automobile engineer and inventor
 Fanny Mendelssohn
1805 - 1847
Composer and pianist of the early Romantic era
Fanny Mendelssohn
1805 - 1847
Composer and pianist of the early Romantic era
 Leni Riefenstahl
1902 - 2003
Nazi propaganda films
Leni Riefenstahl
1902 - 2003
Nazi propaganda films
 Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
1749 - 1832
Writer, poet, scientist, statesman
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
1749 - 1832
Writer, poet, scientist, statesman
 Hans-Georg Gadamer
1900 - 2002
Philosophical hermeneutics
Hans-Georg Gadamer
1900 - 2002
Philosophical hermeneutics
 Frederick III
1831 - 1888
German Emperor and King of Prussia
Frederick III
1831 - 1888
German Emperor and King of Prussia
 Hans Wilhelm Munch
1911 - 2001
SS physician at Auschwitz concentration camp
Hans Wilhelm Munch
1911 - 2001
SS physician at Auschwitz concentration camp
 Karen Horney
1885 - 1952
Psychoanalyst and feminist theorist
Karen Horney
1885 - 1952
Psychoanalyst and feminist theorist
 Rosa Luxemburg
1871 - 1919
Marxist theorist, anti-war activist
Rosa Luxemburg
1871 - 1919
Marxist theorist, anti-war activist
 Luise Rainer
1910 - 2014
Film actress
Luise Rainer
1910 - 2014
Film actress
 Ioan Alexandru
1941 - 2000
Poet, Politician
Ioan Alexandru
1941 - 2000
Poet, Politician
 Nwafor Orizu
1914 - 1999
President of the Nigerian Senate
Nwafor Orizu
1914 - 1999
President of the Nigerian Senate
 Frederica of Hanover
1917 - 1981
Queen consort of Greece
Frederica of Hanover
1917 - 1981
Queen consort of Greece
 Julius Streicher
1885 - 1946
Publisher of Der Stürmer
Julius Streicher
1885 - 1946
Publisher of Der Stürmer
 Martin Heidegger
1889 - 1976
Phenomenology, existentialism, hermeneutics
Martin Heidegger
1889 - 1976
Phenomenology, existentialism, hermeneutics
 Florian Schneider-Esleben
1947 - 2020
Electronic music pioneer
Florian Schneider-Esleben
1947 - 2020
Electronic music pioneer
 Fritz Todt
1891 - 1942
Construction engineer and senior Nazi figure
Fritz Todt
1891 - 1942
Construction engineer and senior Nazi figure
 Martin Camaj
1925 - 1992
Writer and albanologist
Martin Camaj
1925 - 1992
Writer and albanologist
 Romeo Sabourin
1923 - 1944
Spy
Romeo Sabourin
1923 - 1944
Spy
 Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1784 - 1844
Monarch and reformer
Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1784 - 1844
Monarch and reformer
 Safiye Ali
1894 - 1952
Physician
Safiye Ali
1894 - 1952
Physician
 Caspar David Friedrich
1774 - 1840
Romantic landscape painter
Caspar David Friedrich
1774 - 1840
Romantic landscape painter
 Adolf Galland
1912 - 1996
Fighter pilot and commander
Adolf Galland
1912 - 1996
Fighter pilot and commander
 Charlemagne
747 - 814
Emperor of the Romans, King of the Franks
Charlemagne
747 - 814
Emperor of the Romans, King of the Franks
 Dieter Laser
1942 - 2020
Actor
Dieter Laser
1942 - 2020
Actor
 Georg Simmel
1858 - 1918
Sociologist and philosopher
Georg Simmel
1858 - 1918
Sociologist and philosopher
 Franz Anton Mesmer
1734 - 1815
Physician and astronomer
Franz Anton Mesmer
1734 - 1815
Physician and astronomer
 Gertrud Arndt
1903 - 2000
Bauhaus movement
Gertrud Arndt
1903 - 2000
Bauhaus movement
 Wojciech Dlugoraj
1557 - 1619
Renaissance composer and lutenist
Wojciech Dlugoraj
1557 - 1619
Renaissance composer and lutenist
 Robert Bunsen
1811 - 1899
Chemist and inventor
Robert Bunsen
1811 - 1899
Chemist and inventor
 Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
1804 - 1851
Mathematician
Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
1804 - 1851
Mathematician
 Conrad Veidt
1893 - 1943
Silent film star
Conrad Veidt
1893 - 1943
Silent film star
 Friedrich Nietzsche
1844 - 1900
Philosopher, cultural critic, poet, composer
Friedrich Nietzsche
1844 - 1900
Philosopher, cultural critic, poet, composer
 Felix Christian Klein
1849 - 1925
Mathematics professor and educator
Felix Christian Klein
1849 - 1925
Mathematics professor and educator
 Wilhelm von Homburg
1940 - 2004
Actor, boxer, professional wrestler
Wilhelm von Homburg
1940 - 2004
Actor, boxer, professional wrestler
 Diem Brown
1980 - 2014
Reality television personality
Diem Brown
1980 - 2014
Reality television personality
 Johann Pachelbel
1653 - 1706
Composer and organist
Johann Pachelbel
1653 - 1706
Composer and organist
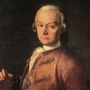 Leopold Mozart
1719 - 1787
Music teacher and composer
Leopold Mozart
1719 - 1787
Music teacher and composer
 Baron Munchausen
1720 - 1797
Nobleman and soldier
Baron Munchausen
1720 - 1797
Nobleman and soldier
 Naziha al Dulaimi
1923 - 2007
founder and first president of the Iraqi Women's
Naziha al Dulaimi
1923 - 2007
founder and first president of the Iraqi Women's
 Otto Dix
1891 - 1969
Expressionist and New Objectivity artist
Otto Dix
1891 - 1969
Expressionist and New Objectivity artist
 Ferdinand Alexander Porsche
1935 - 2012
Porsche designer
Ferdinand Alexander Porsche
1935 - 2012
Porsche designer
 Johann Friedrich Blumenbach
1752 - 1840
Anthropologist and naturalist
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach
1752 - 1840
Anthropologist and naturalist
 Karl Friedrich Schinkel
1781 - 1841
Architect and painter of Neoclassical
Karl Friedrich Schinkel
1781 - 1841
Architect and painter of Neoclassical
 Uta Hagen
1919 - 2004
Actress and theatre practitioner
Uta Hagen
1919 - 2004
Actress and theatre practitioner
 Jenny von Westphalen
1814 - 1881
Theatre critic and political activist
Jenny von Westphalen
1814 - 1881
Theatre critic and political activist
 Gotthold Ephraim Lessing
1729 - 1781
Playwright, critic, and philosopher
Gotthold Ephraim Lessing
1729 - 1781
Playwright, critic, and philosopher
 Alexander von Humboldt
1769 - 1859
Geographer and scientist
Alexander von Humboldt
1769 - 1859
Geographer and scientist
 Alexander Gorchakov
1798 - 1883
Foreign minister of the Russian Empire
Alexander Gorchakov
1798 - 1883
Foreign minister of the Russian Empire
 Jan Nepomucen Bobrowicz
1805 - 1881
Composer, publisher, guitar virtuoso
Jan Nepomucen Bobrowicz
1805 - 1881
Composer, publisher, guitar virtuoso
 Gregor Strasser
1892 - 1934
Nazi Party leader
Gregor Strasser
1892 - 1934
Nazi Party leader
 Wilhelm von Humboldt
1767 - 1835
Philosopher, linguist, diplomat
Wilhelm von Humboldt
1767 - 1835
Philosopher, linguist, diplomat
 Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1884 - 1954
Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
Charles Edward, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
1884 - 1954
Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha
 Otto Heinrich Warburg
1883 - 1970
physiologist and medical doctor
Otto Heinrich Warburg
1883 - 1970
physiologist and medical doctor
 Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff
1900 - 1984
Chief of Personal Staff Reichsführer-SS
Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff
1900 - 1984
Chief of Personal Staff Reichsführer-SS
 Elsa Einstein
1876 - 1936
Second wife and cousin of Albert Einstein
Elsa Einstein
1876 - 1936
Second wife and cousin of Albert Einstein
 Alexandru Ioan Cuza
1820 - 1873
Prince
Alexandru Ioan Cuza
1820 - 1873
Prince
 Charlemagne
747 - 814
Emperor of the Romans and King of the Franks
Charlemagne
747 - 814
Emperor of the Romans and King of the Franks
 Felix Mendelssohn
1809 - 1847
composer, pianist, organist, conductor
Felix Mendelssohn
1809 - 1847
composer, pianist, organist, conductor
 Wilhelm Furtwangler
1886 - 1954
Symphonic and operatic conductor
Wilhelm Furtwangler
1886 - 1954
Symphonic and operatic conductor
 Claus von Stauffenberg
1907 - 1944
Army officer and chief conspirator
Claus von Stauffenberg
1907 - 1944
Army officer and chief conspirator
 Otto Hahn
1879 - 1968
Chemist and pioneer of radioactivity
Otto Hahn
1879 - 1968
Chemist and pioneer of radioactivity
 Prince Maximilian of Baden
1867 - 1929
Chancellor of Germany and Minister
Prince Maximilian of Baden
1867 - 1929
Chancellor of Germany and Minister
 Carl Friedrich Gauss
1777 - 1855
Mathematics and sciences
Carl Friedrich Gauss
1777 - 1855
Mathematics and sciences
 Curd Jurgens
1915 - 1982
Film and stage actor
Curd Jurgens
1915 - 1982
Film and stage actor
 Gustav Knuth
1901 - 1987
Film and theater actor
Gustav Knuth
1901 - 1987
Film and theater actor
 Klemens von Metternich
1773 - 1859
Foreign minister
Klemens von Metternich
1773 - 1859
Foreign minister
 Zahir Howaida
1945 - 2012
Musician, Singer
Zahir Howaida
1945 - 2012
Musician, Singer
 George Grosz
1893 - 1959
Painter, caricaturist, satirist
George Grosz
1893 - 1959
Painter, caricaturist, satirist
 Max Schmeling
1905 - 2005
Heavyweight champion of the world
Max Schmeling
1905 - 2005
Heavyweight champion of the world
 Hans Frank
1900 - 1946
Governor-General of occupied Poland
Hans Frank
1900 - 1946
Governor-General of occupied Poland
 Friedrich Schiller
1759 - 1805
Poet, playwright, historian, philosopher
Friedrich Schiller
1759 - 1805
Poet, playwright, historian, philosopher
 Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
1886 - 1969
Architect and educator
Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
1886 - 1969
Architect and educator
 Helmut Schmidt
1918 - 2015
Chancellor of West Germany
Helmut Schmidt
1918 - 2015
Chancellor of West Germany
 Princess Helena of Waldeck and Pyrmont
1861 - 1922
British royal family member by marriage
Princess Helena of Waldeck and Pyrmont
1861 - 1922
British royal family member by marriage
 Eugenio Coseriu
1921 - 2002
Linguist
Eugenio Coseriu
1921 - 2002
Linguist
 Birol Unel
1961 - 2020
Actor
Birol Unel
1961 - 2020
Actor
 Franz Halder
1884 - 1972
Chief of the Army General Staff
Franz Halder
1884 - 1972
Chief of the Army General Staff
 Sepp Dietrich
1892 - 1966
SS commander and Nazi politician
Sepp Dietrich
1892 - 1966
SS commander and Nazi politician
 Henry Brandon
1912 - 1990
Character actor
Henry Brandon
1912 - 1990
Character actor
 Hermann Klaus Hugo Weyl
1885 - 1955
Mathematics, physics, philosophy
Hermann Klaus Hugo Weyl
1885 - 1955
Mathematics, physics, philosophy
We Need -- admin in