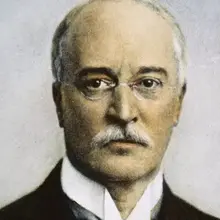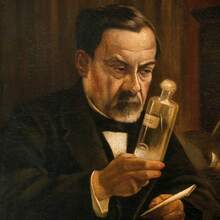Virgil Ierunca
1920 - 2006
Literary critic
Virgil Ierunca
1920 - 2006
Literary critic
 Mathieu Joseph Bonaventure Orfila
1787 - 1853
Founder of toxicology
Mathieu Joseph Bonaventure Orfila
1787 - 1853
Founder of toxicology
 Ali Podrimja
1942 - 2012
Poet and author
Ali Podrimja
1942 - 2012
Poet and author
 Charles Maurice de Talleyrand
1754 - 1838
French secularized clergyman, statesman
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand
1754 - 1838
French secularized clergyman, statesman
 Paul Goma
1935 - 2020
Writer and dissident
Paul Goma
1935 - 2020
Writer and dissident
 Georges Guetary
1915 - 1997
Singer, dancer, cabaret performer and film actor
Georges Guetary
1915 - 1997
Singer, dancer, cabaret performer and film actor
 Olga of Greece and Denmark
1903 - 1997
Princess consort and regent of Yugoslavia
Olga of Greece and Denmark
1903 - 1997
Princess consort and regent of Yugoslavia
 Henri de Saint-Simon
1760 - 1825
Social reformer and founder of Christian socialism
Henri de Saint-Simon
1760 - 1825
Social reformer and founder of Christian socialism
 Louis de Montfort
1673 - 1716
Preacher and missionary apostolic
Louis de Montfort
1673 - 1716
Preacher and missionary apostolic
 Riad Beyrouti
1944 - 2019
Painter and sculptor
Riad Beyrouti
1944 - 2019
Painter and sculptor
 Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
Karl Lagerfeld
1933 - 2019
Creative director of Chanel and Fendi
 France Gall
1947 - 2018
Yé-yé singer and Eurovision winner
France Gall
1947 - 2018
Yé-yé singer and Eurovision winner
 Gregory XI
1329 - 1378
Pope and cardinal
Gregory XI
1329 - 1378
Pope and cardinal
 Josephine Baker
1906 - 1975
Music-hall entertainer and French Resistance agent
Josephine Baker
1906 - 1975
Music-hall entertainer and French Resistance agent
 Clement Juglar
1819 - 1905
Business cycle theory
Clement Juglar
1819 - 1905
Business cycle theory
 Nureddin al-Atassi
1929 - 1992
President of Syria
Nureddin al-Atassi
1929 - 1992
President of Syria
 Suger of France
1081 - 1151
Abbot of Saint-Denis, adviser
Suger of France
1081 - 1151
Abbot of Saint-Denis, adviser
 Alexei Harlamov
1840 - 1925
Painter of portraits, genre scenes
Alexei Harlamov
1840 - 1925
Painter of portraits, genre scenes
 Nubar Pasha
1825 - 1899
Prime Minister of Egypt
Nubar Pasha
1825 - 1899
Prime Minister of Egypt
 Jean Baptiste Kleber
1753 - 1800
General of the French Revolutionary Wars
Jean Baptiste Kleber
1753 - 1800
General of the French Revolutionary Wars
 Leon Dehon
1843 - 1925
Founder of the Congregation of the Sacred Heart
Leon Dehon
1843 - 1925
Founder of the Congregation of the Sacred Heart
 Aleksandra Ekster
1882 - 1949
Painter and designer
Aleksandra Ekster
1882 - 1949
Painter and designer
 Le Thi Luu
1911 - 1988
Painter
Le Thi Luu
1911 - 1988
Painter
 Bernard Maris
1946 - 2015
Economist, writer and journalist
Bernard Maris
1946 - 2015
Economist, writer and journalist
 Roch-Ambroise Cucurron Sicard
1742 - 1822
Instructor of the deaf
Roch-Ambroise Cucurron Sicard
1742 - 1822
Instructor of the deaf
 Cecile Aubry
1928 - 2010
Actress, author, television screenwriter
Cecile Aubry
1928 - 2010
Actress, author, television screenwriter
 Henry Norwest
1881 - 1918
Military Sniper
Henry Norwest
1881 - 1918
Military Sniper
 Iannis Xenakis
1922 - 2001
Composer
Iannis Xenakis
1922 - 2001
Composer
 Maurice Paul Krafft
1946 - 1991
Volcanologist
Maurice Paul Krafft
1946 - 1991
Volcanologist
 Anthony Bourdain
1956 - 2018
American chef and presenter
Anthony Bourdain
1956 - 2018
American chef and presenter
 George Enescu
1881 - 1955
Composer
George Enescu
1881 - 1955
Composer
 Francois Fenelon
1651 - 1715
Archbishop of Cambrai, author of The Adventures
Francois Fenelon
1651 - 1715
Archbishop of Cambrai, author of The Adventures
 Diana Princess of Wales
1961 - 1997
Diana Princess of Wales
1961 - 1997
 Constantine Samuel Rafinesque
1783 - 1840
Botanist and zoologist
Constantine Samuel Rafinesque
1783 - 1840
Botanist and zoologist
 Emile Zola
1840 - 1902
Naturalist writer and Dreyfusard activist
Emile Zola
1840 - 1902
Naturalist writer and Dreyfusard activist
 Alexandru Proca
1897 - 1955
Physicist
Alexandru Proca
1897 - 1955
Physicist
 Anatoly Lunacharsky
1875 - 1933
First Soviet People's Commissar of Education
Anatoly Lunacharsky
1875 - 1933
First Soviet People's Commissar of Education
 Marcel Proust
1871 - 1922
Novelist and critic
Marcel Proust
1871 - 1922
Novelist and critic
 Bozidar Kantuser
1921 - 1999
Composer
Bozidar Kantuser
1921 - 1999
Composer
 Ginger Baker
1939 - 2019
Drummer of Cream,and Ginger Baker's Air Force
Ginger Baker
1939 - 2019
Drummer of Cream,and Ginger Baker's Air Force
 Petru Dumitriu
1924 - 2002
Novelist
Petru Dumitriu
1924 - 2002
Novelist
 Claude La Colombiere
1641 - 1682
Priest and confessor of Margaret Mary Alacoque
Claude La Colombiere
1641 - 1682
Priest and confessor of Margaret Mary Alacoque
 Federica Montseny
1905 - 1994
Anarchist leader, novelist,writer on social issues
Federica Montseny
1905 - 1994
Anarchist leader, novelist,writer on social issues
 Alina Szapocznikow
1926 - 1973
Sculptor and graphic artist
Alina Szapocznikow
1926 - 1973
Sculptor and graphic artist
 Gregory of Tours
538 - 594
Historian and Bishop of Tours
Gregory of Tours
538 - 594
Historian and Bishop of Tours
 Nemir Kirdar
1936 - 2020
Founder and CEO of Investcorp
Nemir Kirdar
1936 - 2020
Founder and CEO of Investcorp
 Don Raimundo
1090 - 1152
Archbishop of Toledo and patron of the Toledan
Don Raimundo
1090 - 1152
Archbishop of Toledo and patron of the Toledan
 Garcilaso de la Vega
1562 - 1635
Playwright and poet of the Spanish Golden Age
Garcilaso de la Vega
1562 - 1635
Playwright and poet of the Spanish Golden Age
 Germaine Dulac
1882 - 1942
Film director, film theorist
Germaine Dulac
1882 - 1942
Film director, film theorist
 Pridi Phanomyong
1900 - 1983
Prime Minister
Pridi Phanomyong
1900 - 1983
Prime Minister
 Albert Schweitzer
1875 - 1965
Founder of the Albert Schweitzer Hospital
Albert Schweitzer
1875 - 1965
Founder of the Albert Schweitzer Hospital
 Mai Trung Thu
1906 - 1980
Painter
Mai Trung Thu
1906 - 1980
Painter
 Charles de Gaulle
1890 - 1970
President of France
Charles de Gaulle
1890 - 1970
President of France
 Peter Wooldridge Townsend
1914 - 1995
RAF officer and courtier
Peter Wooldridge Townsend
1914 - 1995
RAF officer and courtier
 Richard Anthony
1938 - 2015
French pop singer
Richard Anthony
1938 - 2015
French pop singer
 Naim Kattan
1928 - 2021
Novelist, essayist and critic
Naim Kattan
1928 - 2021
Novelist, essayist and critic
 Erik Satie
1866 - 1925
Composer and pianist
Erik Satie
1866 - 1925
Composer and pianist
 Mariano Eduardo de Rivero y Ustariz
1798 - 1857
scientist
Mariano Eduardo de Rivero y Ustariz
1798 - 1857
scientist
 Claude Monet
1840 - 1926
Founder of impressionist painting
Claude Monet
1840 - 1926
Founder of impressionist painting
 Vincent van Gogh
1853 - 1890
Vincent van Gogh
1853 - 1890
 Marguerite Duras
1914 - 1996
novelist
Marguerite Duras
1914 - 1996
novelist
 Germanus of Auxerre
378 - 445
Bishop of Autissiodorum and defender of orthodoxy
Germanus of Auxerre
378 - 445
Bishop of Autissiodorum and defender of orthodoxy
 Palladius
365 - 457
Bishop of Ireland
Palladius
365 - 457
Bishop of Ireland
 Maurice Allais
1911 - 2010
Nobel laureate in economics
Maurice Allais
1911 - 2010
Nobel laureate in economics
 Andre Coindre
1787 - 1826
Founder of the Brothers of the Sacred Heart
Andre Coindre
1787 - 1826
Founder of the Brothers of the Sacred Heart
 Robert Palmer
1949 - 2003
Singer, songwriter, record producer
Robert Palmer
1949 - 2003
Singer, songwriter, record producer
 Mikhail Larionov
1881 - 1964
Painter and stage designer
Mikhail Larionov
1881 - 1964
Painter and stage designer
 Louis-Andre de Grimaldi
1736 - 1804
Bishop of Le Mans and Noyon, Peer of France
Louis-Andre de Grimaldi
1736 - 1804
Bishop of Le Mans and Noyon, Peer of France
 Arnulf of Metz
582 - 640
Bishop of Metz and advisor to the Merovingian
Arnulf of Metz
582 - 640
Bishop of Metz and advisor to the Merovingian
 Jules Gabriel Verne
1828 - 1905
Writer of science fiction and adventure novels
Jules Gabriel Verne
1828 - 1905
Writer of science fiction and adventure novels
 Francis I of France
1494 - 1547
king of France and patron of the arts
Francis I of France
1494 - 1547
king of France and patron of the arts
 Maria d'Apparecida
1926 - 2017
Abstract painter
Maria d'Apparecida
1926 - 2017
Abstract painter
 Konstantin Korovin
1861 - 1939
Painter of landscapes, portraits
Konstantin Korovin
1861 - 1939
Painter of landscapes, portraits
 Samuel Beckett
1906 - 1989
Nobel laureate in literature
Samuel Beckett
1906 - 1989
Nobel laureate in literature
 Georges Moustaki
1934 - 2013
Singer-songwriter
Georges Moustaki
1934 - 2013
Singer-songwriter
 Rene Descartes
1596 - 1650
Founder of modern philosophy and analytic geometry
Rene Descartes
1596 - 1650
Founder of modern philosophy and analytic geometry
 Eleanor of Aquitaine
1122 - 1204
Queen consort of France and England
Eleanor of Aquitaine
1122 - 1204
Queen consort of France and England
 Bernard Gui
1261 - 1331
Inquisitor of heresy in Languedoc
Bernard Gui
1261 - 1331
Inquisitor of heresy in Languedoc
 Louis The Pious
778 - 840
Emperor of the Franks
Louis The Pious
778 - 840
Emperor of the Franks
 Coco Chanel
1883 - 1971
Fashion designer and founder of Chanel brand
Coco Chanel
1883 - 1971
Fashion designer and founder of Chanel brand
 Jean de Labadie
1610 - 1674
Founder of the Labadists
Jean de Labadie
1610 - 1674
Founder of the Labadists
 Henri Gregoire
1750 - 1831
Constitutional bishop of Blois
Henri Gregoire
1750 - 1831
Constitutional bishop of Blois
 Musidora
1889 - 1957
Acting in silent film
Musidora
1889 - 1957
Acting in silent film
 Louis XVI of France
1754 - 1793
King of France and Navarre, King of the French
Louis XVI of France
1754 - 1793
King of France and Navarre, King of the French
 Olivia de Havilland
1916 - 2020
Actress of Hollywood’s Golden Age
Olivia de Havilland
1916 - 2020
Actress of Hollywood’s Golden Age
 Jean de Brebeuf
1593 - 1649
Jesuit priest and missionary to the Huron people
Jean de Brebeuf
1593 - 1649
Jesuit priest and missionary to the Huron people
 Pope Stephen IX
1057 - 1158
Head of the Catholic Church
Pope Stephen IX
1057 - 1158
Head of the Catholic Church
 John McCrae
1872 - 1918
Poet, Physician, Soldier
John McCrae
1872 - 1918
Poet, Physician, Soldier
 Bernard of Clairvaux
1090 - 1153
Cistercian monk
Bernard of Clairvaux
1090 - 1153
Cistercian monk
 Felix of Valois
1127 - 1212
Co-founder of the Trinitarian Order
Felix of Valois
1127 - 1212
Co-founder of the Trinitarian Order
 Marie Salome Skudofska Curie
1867 - 1934
Physicist chemist
Marie Salome Skudofska Curie
1867 - 1934
Physicist chemist
 Aaron Jean-Marie Lustiger
1926 - 2007
Archbishop of Paris
Aaron Jean-Marie Lustiger
1926 - 2007
Archbishop of Paris
 Louis Pasteur
1822 - 1895
Chemist and microbiologist
Louis Pasteur
1822 - 1895
Chemist and microbiologist
 Anne of Brittany
1477 - 1514
Duchess of Brittany and Queen of France
Anne of Brittany
1477 - 1514
Duchess of Brittany and Queen of France
 Blaise Pascal
1623 - 1662
Mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher
Blaise Pascal
1623 - 1662
Mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher
 Salah al-Din Bitar
1912 - 1980
Politician
Salah al-Din Bitar
1912 - 1980
Politician
 Maria Bashkirtseva
1858 - 1884
Portraits and cityscapes
Maria Bashkirtseva
1858 - 1884
Portraits and cityscapes
 Jerome-Adolphe Blanqui
1798 - 1854
Economic historian and liberal economist
Jerome-Adolphe Blanqui
1798 - 1854
Economic historian and liberal economist
 Alexandre Benois
1870 - 1960
Art critic and historian
Alexandre Benois
1870 - 1960
Art critic and historian
 Horatiu Radulescu
1942 - 2008
composer
Horatiu Radulescu
1942 - 2008
composer
 Alexander Briullov
1798 - 1877
Art critic and historian
Alexander Briullov
1798 - 1877
Art critic and historian
 Alfred Firmin Loisy
1857 - 1940
Biblical scholar and critic of traditional views
Alfred Firmin Loisy
1857 - 1940
Biblical scholar and critic of traditional views
 Ulfat Idlibi
1912 - 2007
Novelist
Ulfat Idlibi
1912 - 2007
Novelist
 Raoul Coutard
1924 - 2016
Cinematographer for French New Wave directors
Raoul Coutard
1924 - 2016
Cinematographer for French New Wave directors
 Constantin Virgil Gheorghiu
1916 - 1992
Writer
Constantin Virgil Gheorghiu
1916 - 1992
Writer
 Bernard de Montfaucon
1655 - 1741
Paleographer and archaeologist
Bernard de Montfaucon
1655 - 1741
Paleographer and archaeologist
 Eugen Ionescu
1909 - 1994
Playwright
Eugen Ionescu
1909 - 1994
Playwright
 Henri Breuil
1877 - 1961
Authority on prehistoric cave art
Henri Breuil
1877 - 1961
Authority on prehistoric cave art
 Charles Aznavour
1924 - 2018
Singer, songwriter, actor and diplomat
Charles Aznavour
1924 - 2018
Singer, songwriter, actor and diplomat
 Bulat Okudzhava
1924 - 1997
Author song singer-songwriter
Bulat Okudzhava
1924 - 1997
Author song singer-songwriter
 Alice Guy-Blache
1873 - 1968
Pioneer of the French and American film industries
Alice Guy-Blache
1873 - 1968
Pioneer of the French and American film industries
 Sania Saleh
1935 - 1985
Poet and writer
Sania Saleh
1935 - 1985
Poet and writer
 Charles-Michel de l'Epee
1712 - 1789
Founder of the first public school for the deaf
Charles-Michel de l'Epee
1712 - 1789
Founder of the first public school for the deaf
 Nicolas Malebranche
1638 - 1715
Rationalist philosopher and theologian
Nicolas Malebranche
1638 - 1715
Rationalist philosopher and theologian
 Jean Meslier
1664 - 1729
Priest and author of a book
Jean Meslier
1664 - 1729
Priest and author of a book
 Krzysztof Gawedzki
1947 - 2022
Mathematical physics
Krzysztof Gawedzki
1947 - 2022
Mathematical physics
 Johnny Hallyday
1943 - 2017
Singer-songwriter and actor
Johnny Hallyday
1943 - 2017
Singer-songwriter and actor
 Sacha Distel
1933 - 2004
Singer, guitarist, songwriter and actor
Sacha Distel
1933 - 2004
Singer, guitarist, songwriter and actor
 John Baptist de La Salle
1651 - 1719
Founder of the Institute of Brothers of Christian
John Baptist de La Salle
1651 - 1719
Founder of the Institute of Brothers of Christian
 Jean Joseph Marie Amiot
1718 - 1793
Jesuit missionary and translator
Jean Joseph Marie Amiot
1718 - 1793
Jesuit missionary and translator
 Victor Hugo
1802 - 1885
Romantic writer and politician
Victor Hugo
1802 - 1885
Romantic writer and politician
 Savitri Devi
1905 - 1982
Proponent of Nazism and Hinduism
Savitri Devi
1905 - 1982
Proponent of Nazism and Hinduism
 Jean du Vergier de Hauranne
1581 - 1643
Jansenism leader
Jean du Vergier de Hauranne
1581 - 1643
Jansenism leader
 Karl Brandt
1904 - 1948
Personal physician of Adolf Hitler
Karl Brandt
1904 - 1948
Personal physician of Adolf Hitler
 Pierre de Berulle
1575 - 1629
Founder of the French school of spirituality
Pierre de Berulle
1575 - 1629
Founder of the French school of spirituality
 Max Ernst
1891 - 1976
Painter, sculptor, poet
Max Ernst
1891 - 1976
Painter, sculptor, poet
 Marie Bell
1900 - 1985
Tragedian, comic actor, stage director
Marie Bell
1900 - 1985
Tragedian, comic actor, stage director
 Maria Blanchard
1881 - 1932
Painter and pioneer of Cubism
Maria Blanchard
1881 - 1932
Painter and pioneer of Cubism
 Tristan Tzara
1896 - 1963
Poet, Essayist
Tristan Tzara
1896 - 1963
Poet, Essayist
 Peter Dmytruk
1920 - 1943
Sergeant in the Royal Canadian Air Force
Peter Dmytruk
1920 - 1943
Sergeant in the Royal Canadian Air Force
 Henry IV of France
1553 - 1610
King of France and Navarre, leader
Henry IV of France
1553 - 1610
King of France and Navarre, leader
 Michel Kilo
1940 - 2021
writer and human rights activist
Michel Kilo
1940 - 2021
writer and human rights activist
 Jean-Baptiste Colbert
1619 - 1683
minister of finance and navy under Louis XIV
Jean-Baptiste Colbert
1619 - 1683
minister of finance and navy under Louis XIV
 Lily Pons
1898 - 1976
Opera singer and actress
Lily Pons
1898 - 1976
Opera singer and actress
 Marius Constant
1925 - 2004
Composer, Conductor
Marius Constant
1925 - 2004
Composer, Conductor
 Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci
1452 - 1519
Painting, Engineering, Anatomical studies
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci
1452 - 1519
Painting, Engineering, Anatomical studies
 Jean-Baptiste Say
1767 - 1832
Political economy, Say's law, entrepreneurship
Jean-Baptiste Say
1767 - 1832
Political economy, Say's law, entrepreneurship
 Mai Skaf
1969 - 2018
Actress and activist
Mai Skaf
1969 - 2018
Actress and activist
 Alberto Cavalcanti
1897 - 1982
Film director and producer
Alberto Cavalcanti
1897 - 1982
Film director and producer
 Vu Cao Dam
1908 - 2000
Painter, Sculptor
Vu Cao Dam
1908 - 2000
Painter, Sculptor
 Louis Cappel
1585 - 1658
Protestant churchman and scholar
Louis Cappel
1585 - 1658
Protestant churchman and scholar
 Eugenia Osterberger
1852 - 1932
Composer and pianist
Eugenia Osterberger
1852 - 1932
Composer and pianist
 Charles Trenet
1913 - 2001
Singer and songwriter
Charles Trenet
1913 - 2001
Singer and songwriter
 Marlene Dietrich
1901 - 1992
Movie star and cabaret performer
Marlene Dietrich
1901 - 1992
Movie star and cabaret performer
 Peter Chanel
1803 - 1841
Catholic priest, missionary, and martyr
Peter Chanel
1803 - 1841
Catholic priest, missionary, and martyr
 Urbain Grandier
1590 - 1634
Priest and alleged sorcerer
Urbain Grandier
1590 - 1634
Priest and alleged sorcerer
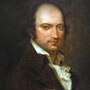 Andre Chenier
1762 - 1794
Poet and political journalist
Andre Chenier
1762 - 1794
Poet and political journalist
 Prosper Gueranger
1805 - 1875
Benedictine abbot and liturgist
Prosper Gueranger
1805 - 1875
Benedictine abbot and liturgist
 Niccolo Paganini
1782 - 1840
Violinist
Niccolo Paganini
1782 - 1840
Violinist
 Francisco Goya
1746 - 1828
Painter and printmaker
Francisco Goya
1746 - 1828
Painter and printmaker
We Need -- admin in