Ishiro Honda
1911 - 1993
Director and co-creator of the Godzilla franchise
Ishiro Honda
1911 - 1993
Director and co-creator of the Godzilla franchise
 Kido Takayoshi
1833 - 1877
One of the leaders of the Meiji Restoration
Kido Takayoshi
1833 - 1877
One of the leaders of the Meiji Restoration
 Togo Heihachiro
1848 - 1934
Admiral of the fleet in the Imperial Japanese Navy
Togo Heihachiro
1848 - 1934
Admiral of the fleet in the Imperial Japanese Navy
 Soichiro Honda
1906 - 1991
Founder of Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
Soichiro Honda
1906 - 1991
Founder of Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
 Junko Tabei
1939 - 2016
First woman to summit Mount Everest
Junko Tabei
1939 - 2016
First woman to summit Mount Everest
 Hasekura Tsunenaga
1571 - 1622
Leader of the Keichō Embassy
Hasekura Tsunenaga
1571 - 1622
Leader of the Keichō Embassy
 Toyotomi Hideyori
1593 - 1615
Samurai lord, last scion of the Toyotomi clan
Toyotomi Hideyori
1593 - 1615
Samurai lord, last scion of the Toyotomi clan
 Mitsumasa Yonai
1880 - 1948
Navy admiral and Prime Minister of Japan
Mitsumasa Yonai
1880 - 1948
Navy admiral and Prime Minister of Japan
 Norio Ohga
1930 - 2011
Former president and chairman of Sony Corporation
Norio Ohga
1930 - 2011
Former president and chairman of Sony Corporation
 Hana Kimura
1997 - 2020
Professional wrestler
Hana Kimura
1997 - 2020
Professional wrestler
 Emperor Kanmu
735 - 806
Emperor of Japan
Emperor Kanmu
735 - 806
Emperor of Japan
 Kuroda Seiki
1866 - 1924
Western-style painter
Kuroda Seiki
1866 - 1924
Western-style painter
 Kaneto Shindo
1912 - 2012
Film director, screenwriter, film producer, writer
Kaneto Shindo
1912 - 2012
Film director, screenwriter, film producer, writer
 Tadamichi Kuribayashi
1891 - 1945
Commander of the Japanese garrison at the Battle
Tadamichi Kuribayashi
1891 - 1945
Commander of the Japanese garrison at the Battle
 Ichiyo Higuchi
1872 - 1896
Writer and poet
Ichiyo Higuchi
1872 - 1896
Writer and poet
 Mako Iwamatsu
1933 - 2006
Actor and voice actor
Mako Iwamatsu
1933 - 2006
Actor and voice actor
 Kenji Mizoguchi
1898 - 1956
Film director and screenwriter
Kenji Mizoguchi
1898 - 1956
Film director and screenwriter
 Tokugawa Iemitsu
1604 - 1651
Third shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty
Tokugawa Iemitsu
1604 - 1651
Third shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty
 Hanzo HATTORI
1542 - 1596
Ninja master and tactician
Hanzo HATTORI
1542 - 1596
Ninja master and tactician
 Hiroo Onoda
1922 - 2014
Imperial Japanese Army intelligence officer
Hiroo Onoda
1922 - 2014
Imperial Japanese Army intelligence officer
 Masako Natsume
1957 - 1985
portrayal of Tripitaka in the TV series Monkey
Masako Natsume
1957 - 1985
portrayal of Tripitaka in the TV series Monkey
 Wong Ka Kui
1962 - 1993
Hong Kong musician, singer and songwriter
Wong Ka Kui
1962 - 1993
Hong Kong musician, singer and songwriter
 Yasuhiro Nakasone
1918 - 2019
Prime Minister of Japan
Yasuhiro Nakasone
1918 - 2019
Prime Minister of Japan
 Masaru Ibuka
1908 - 1997
Co-founder of Sony
Masaru Ibuka
1908 - 1997
Co-founder of Sony
 Morihei Ueshiba
1883 - 1969
Founder of aikido
Morihei Ueshiba
1883 - 1969
Founder of aikido
 Tokugawa Tsunayoshi
1646 - 1709
Fifth shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty
Tokugawa Tsunayoshi
1646 - 1709
Fifth shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty
 Saionji Kinmochi
1849 - 1940
Prime Minister of Japan
Saionji Kinmochi
1849 - 1940
Prime Minister of Japan
 Fujiko Fujio
1933 - 1996
manga artist and screenwriter
Fujiko Fujio
1933 - 1996
manga artist and screenwriter
 Takashi Shimura
1905 - 1982
Actor in Akira Kurosawa's films
Takashi Shimura
1905 - 1982
Actor in Akira Kurosawa's films
 Takahashi Korekiyo
1854 - 1936
Prime Minister of Japan and Minister of Finance
Takahashi Korekiyo
1854 - 1936
Prime Minister of Japan and Minister of Finance
 Emperor Suinin
-69 - 7
Emperor of Japan
Emperor Suinin
-69 - 7
Emperor of Japan
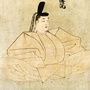 Emperor Sutoku
1119 - 1164
Emperor of Japan
Emperor Sutoku
1119 - 1164
Emperor of Japan
 Matsuo Basho
1644 - 1694
Haiku poet and traveler
Matsuo Basho
1644 - 1694
Haiku poet and traveler
 Nichiren
1222 - 1282
Buddhist priest and philosopher
Nichiren
1222 - 1282
Buddhist priest and philosopher
 Fukuzawa Yukichi
1835 - 1901
Founder of Keio University and Jiji-Shinpō
Fukuzawa Yukichi
1835 - 1901
Founder of Keio University and Jiji-Shinpō
 Masanobu Tsuji
1901 - 1961
Army officer and tactical planner
Masanobu Tsuji
1901 - 1961
Army officer and tactical planner
 Kitagawa Utamaro
1753 - 1806
Woodblock printmaker and painter
Kitagawa Utamaro
1753 - 1806
Woodblock printmaker and painter
 Koichi Kido
1889 - 1977
Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal of Japan
Koichi Kido
1889 - 1977
Lord Keeper of the Privy Seal of Japan
 Fumimaro Konoe
1891 - 1945
Prime Minister of Japan
Fumimaro Konoe
1891 - 1945
Prime Minister of Japan
 Sugawara Michizane
845 - 903
Scholar, poet, and politician
Sugawara Michizane
845 - 903
Scholar, poet, and politician
 Utagawa Hiroshige
1797 - 1858
Ukiyo-e artist and printmaker
Utagawa Hiroshige
1797 - 1858
Ukiyo-e artist and printmaker
 Ken Takakura
1931 - 2014
Yakuza and action films
Ken Takakura
1931 - 2014
Yakuza and action films
 Tokugawa Yoshinobu
1837 - 1913
The last shogun of Japan
Tokugawa Yoshinobu
1837 - 1913
The last shogun of Japan
 Emperor Shomu
701 - 756
Emperor of Japan
Emperor Shomu
701 - 756
Emperor of Japan
 Shizo Kanakuri
1891 - 1983
Marathon runner and one of the early leaders
Shizo Kanakuri
1891 - 1983
Marathon runner and one of the early leaders
 Yasuko Namba
1949 - 1996
Businesswoman and climber
Yasuko Namba
1949 - 1996
Businesswoman and climber
 Kobo Abe
1924 - 1993
Novelist, playwright, photographer, inventor
Kobo Abe
1924 - 1993
Novelist, playwright, photographer, inventor
 Nagisa Oshima
1932 - 2013
Film director and screenwriter
Nagisa Oshima
1932 - 2013
Film director and screenwriter
 Chiyonofuji Mitsugu
1955 - 2016
Sumo wrestler and the 58th yokozuna
Chiyonofuji Mitsugu
1955 - 2016
Sumo wrestler and the 58th yokozuna
 Saito Makoto
1858 - 1936
Prime Minister of Japan, Governor-General of Korea
Saito Makoto
1858 - 1936
Prime Minister of Japan, Governor-General of Korea
 Yusaku Matsuda
1949 - 1989
Action film star and television detective
Yusaku Matsuda
1949 - 1989
Action film star and television detective
 Shumei Okawa
1886 - 1957
Political theorist, historian, Islamic scholar
Shumei Okawa
1886 - 1957
Political theorist, historian, Islamic scholar
 Isao Tomita
1932 - 2016
Electronic music pioneer
Isao Tomita
1932 - 2016
Electronic music pioneer
 Akiko Yosano
1878 - 1942
Poet, writer, educator, social reformer
Akiko Yosano
1878 - 1942
Poet, writer, educator, social reformer
 Takashi Amano
1954 - 2015
Aquascaping and nature photography
Takashi Amano
1954 - 2015
Aquascaping and nature photography
 Imagawa Yoshimoto
1519 - 1560
Feudal lord of Suruga, Totomi
Imagawa Yoshimoto
1519 - 1560
Feudal lord of Suruga, Totomi
 Emperor Go Momozono
1758 - 1779
Emperor of Japan from 1771 to 1779
Emperor Go Momozono
1758 - 1779
Emperor of Japan from 1771 to 1779
 Tomisaburo Wakayama
1929 - 1992
Playing Ogami Itto in the Lone Wolf
Tomisaburo Wakayama
1929 - 1992
Playing Ogami Itto in the Lone Wolf
 Daisetsu Teitaro Suzuki
1870 - 1966
Zen scholar and translator
Daisetsu Teitaro Suzuki
1870 - 1966
Zen scholar and translator
 Okita Soji
1802 - 1868
Captain of the first unit of the Shinsengumi
Okita Soji
1802 - 1868
Captain of the first unit of the Shinsengumi
 Toshiki Kaifu
1931 - 2022
Prime minister of Japan
Toshiki Kaifu
1931 - 2022
Prime minister of Japan
 Kinji Fukasaku
1930 - 2003
Director and screenwriter of yakuza and dystopian
Kinji Fukasaku
1930 - 2003
Director and screenwriter of yakuza and dystopian
 Daijiro Kato
1976 - 2003
Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
Daijiro Kato
1976 - 2003
Grand Prix motorcycle road racer
 Prince Naruhiko Higashikuni
1887 - 1990
Imperial prince and army general
Prince Naruhiko Higashikuni
1887 - 1990
Imperial prince and army general
 Gunpei Yokoi
1941 - 1997
Creator of Game Boy and Game & Watch
Gunpei Yokoi
1941 - 1997
Creator of Game Boy and Game & Watch
 Masanobu Fukuoka
1913 - 2008
natural farming and re-vegetation of desertified
Masanobu Fukuoka
1913 - 2008
natural farming and re-vegetation of desertified
 Akira Kurosawa
1910 - 1998
Film director, screenwriter, producer, editor
Akira Kurosawa
1910 - 1998
Film director, screenwriter, producer, editor
 Jigoro Kano
1860 - 1938
Founder of judo and first Asian member of the IOC
Jigoro Kano
1860 - 1938
Founder of judo and first Asian member of the IOC
 Terauchi Masatake
1852 - 1919
Prime Minister of Japan
Terauchi Masatake
1852 - 1919
Prime Minister of Japan
 Jun'ichiro Tanizaki
1886 - 1965
Modern Japanese literature
Jun'ichiro Tanizaki
1886 - 1965
Modern Japanese literature
 Hideki Tojo
1884 - 1948
General of the Imperial Japanese Army
Hideki Tojo
1884 - 1948
General of the Imperial Japanese Army
 Koxinga
1624 - 1662
Southern Ming general and ruler of Taiwan
Koxinga
1624 - 1662
Southern Ming general and ruler of Taiwan
 Haruma Miura
1990 - 2020
Actor and singer
Haruma Miura
1990 - 2020
Actor and singer
 Minamoto no Yoshitsune
1159 - 1189
Military commander of the Minamoto clan
Minamoto no Yoshitsune
1159 - 1189
Military commander of the Minamoto clan
 Izumo no Okuni
1578 - 1613
Founder of kabuki theatre
Izumo no Okuni
1578 - 1613
Founder of kabuki theatre
 Emperor Antoku
1178 - 1185
81st emperor of Japan
Emperor Antoku
1178 - 1185
81st emperor of Japan
 Ii Naomasa
1561 - 1602
General under Tokugawa Ieyasu
Ii Naomasa
1561 - 1602
General under Tokugawa Ieyasu
 Jiro Horikoshi
1903 - 1982
Chief engineer of Mitsubishi A6M Zero fighter
Jiro Horikoshi
1903 - 1982
Chief engineer of Mitsubishi A6M Zero fighter
 Satoshi Kon
1963 - 2010
Anime director and manga artist
Satoshi Kon
1963 - 2010
Anime director and manga artist
 Chuya Nakahara
1907 - 1937
Poet, translator
Chuya Nakahara
1907 - 1937
Poet, translator
 Antonio Inoki
1943 - 2022
Professional wrestler and mixed martial artist
Antonio Inoki
1943 - 2022
Professional wrestler and mixed martial artist
 Tokugawa Ieyasu
1543 - 1616
Shogun of Japan, founder of the Tokugawa shogunate
Tokugawa Ieyasu
1543 - 1616
Shogun of Japan, founder of the Tokugawa shogunate
 Tamon Yamaguchi
1892 - 1942
Naval officer and commander
Tamon Yamaguchi
1892 - 1942
Naval officer and commander
 Kyu Sakamoto
1941 - 1985
Singer and actor
Kyu Sakamoto
1941 - 1985
Singer and actor
 Ashikaga Yoshimitsu
1358 - 1408
Shogun of the Ashikaga shogunate
Ashikaga Yoshimitsu
1358 - 1408
Shogun of the Ashikaga shogunate
 Kiichiro Toyoda
1894 - 1952
Founder and CEO of Toyota Motor Corporation
Kiichiro Toyoda
1894 - 1952
Founder and CEO of Toyota Motor Corporation
 Sanada Nobushige
1567 - 1615
Leading general of the Siege of Osaka
Sanada Nobushige
1567 - 1615
Leading general of the Siege of Osaka
 Iwane Matsui
1878 - 1948
Commander of the expeditionary force sent to China
Iwane Matsui
1878 - 1948
Commander of the expeditionary force sent to China
 Maurice Paul Krafft
1946 - 1991
Volcanologist
Maurice Paul Krafft
1946 - 1991
Volcanologist
 Sonny Chiba
1939 - 2021
martial arts cinema star
Sonny Chiba
1939 - 2021
martial arts cinema star
 Kijuro Shidehara
1872 - 1951
Prime minister of Japan
Kijuro Shidehara
1872 - 1951
Prime minister of Japan
 Kakuei Tanaka
1918 - 1993
Prime Minister of Japan
Kakuei Tanaka
1918 - 1993
Prime Minister of Japan
 Sadao Araki
1877 - 1966
General in the Imperial Japanese Army and Minister
Sadao Araki
1877 - 1966
General in the Imperial Japanese Army and Minister
 Empress Kojun
1903 - 2000
Empress consort of Japan
Empress Kojun
1903 - 2000
Empress consort of Japan
 Emperor Sakuramachi
1720 - 1750
Emperor of Japan from 1735 to 1747
Emperor Sakuramachi
1720 - 1750
Emperor of Japan from 1735 to 1747
 Kenzo Tange
1913 - 2005
Architect and urban planner
Kenzo Tange
1913 - 2005
Architect and urban planner
 Shigeru Yoshida
1878 - 1967
Prime minister of Japan
Shigeru Yoshida
1878 - 1967
Prime minister of Japan
 Hideki Irabu
1969 - 2011
Pitcher
Hideki Irabu
1969 - 2011
Pitcher
 Kirin Kiki
1943 - 2018
Actress for Japanese cinema and television
Kirin Kiki
1943 - 2018
Actress for Japanese cinema and television
 Tokugawa Iemochi
1846 - 1866
14th shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate
Tokugawa Iemochi
1846 - 1866
14th shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate
 Son Byong-hi
1861 - 1922
Third leader of Donghak (Eastern learning)
Son Byong-hi
1861 - 1922
Third leader of Donghak (Eastern learning)
 Ryutaro Hashimoto
1937 - 2006
Prime minister of Japan
Ryutaro Hashimoto
1937 - 2006
Prime minister of Japan
 Ashikaga Takauji
1305 - 1358
Shogun and founder of the Ashikaga shogunate
Ashikaga Takauji
1305 - 1358
Shogun and founder of the Ashikaga shogunate
 Hiromi Hayakawa
1982 - 2017
Musical theatre
Hiromi Hayakawa
1982 - 2017
Musical theatre
 Fusajiro Yamauchi
1859 - 1940
Founder of Nintendo
Fusajiro Yamauchi
1859 - 1940
Founder of Nintendo
 Toyotomi Hideyoshi
1537 - 1598
Feudal lord and chief Imperial minister
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
1537 - 1598
Feudal lord and chief Imperial minister
 Mitsuharu Misawa
1962 - 2009
Professional wrestler and promoter
Mitsuharu Misawa
1962 - 2009
Professional wrestler and promoter
 Gichin Funakoshi
1868 - 1957
Founder of Shotokan Karate
Gichin Funakoshi
1868 - 1957
Founder of Shotokan Karate
 Isoroku Yamamoto
1884 - 1943
Admiral of the Imperial Japanese Navy
Isoroku Yamamoto
1884 - 1943
Admiral of the Imperial Japanese Navy
 Chishu Ryu
1904 - 1993
Film actor
Chishu Ryu
1904 - 1993
Film actor
 Akiyuki Nosaka
1930 - 2015
Novelist, singer, lyricist
Akiyuki Nosaka
1930 - 2015
Novelist, singer, lyricist
 Akira Yoshizawa
1911 - 2005
Origami master
Akira Yoshizawa
1911 - 2005
Origami master
 Tomoyuki Yamashita
1885 - 1946
General in the Imperial Japanese Army
Tomoyuki Yamashita
1885 - 1946
General in the Imperial Japanese Army
 Akio Morita
1921 - 1999
Co-founder of Sony
Akio Morita
1921 - 1999
Co-founder of Sony
 Ishida Mitsunari
1559 - 1600
Commander of the Western army in the Battle
Ishida Mitsunari
1559 - 1600
Commander of the Western army in the Battle
 Shu Uemura
1928 - 2007
Makeup artist and founder of Shu Uemura Cosmetics
Shu Uemura
1928 - 2007
Makeup artist and founder of Shu Uemura Cosmetics
 Sen Rikyu
1522 - 1591
Tea master who perfected the tea ceremony
Sen Rikyu
1522 - 1591
Tea master who perfected the tea ceremony
 Eisaku Sato
1901 - 1975
Prime Minister of Japan
Eisaku Sato
1901 - 1975
Prime Minister of Japan
 Norifumi Yamamoto
1977 - 2018
Mixed martial artist and kickboxer
Norifumi Yamamoto
1977 - 2018
Mixed martial artist and kickboxer
 Juzo Itami
1933 - 1997
Film director, screenwriter, actor
Juzo Itami
1933 - 1997
Film director, screenwriter, actor
 Hideki Yukawa
1907 - 1981
Theoretical physicist and meson theory
Hideki Yukawa
1907 - 1981
Theoretical physicist and meson theory
 Emperor Go-Sai
1638 - 1685
Emperor of Japan
Emperor Go-Sai
1638 - 1685
Emperor of Japan
 Mitsuru Ushijima
1887 - 1945
Commander of the 32nd Army in the Battle
Mitsuru Ushijima
1887 - 1945
Commander of the 32nd Army in the Battle
 Korechika Anami
1887 - 1945
General in the Imperial Japanese Army
Korechika Anami
1887 - 1945
General in the Imperial Japanese Army
 Uesugi Kenshin
1530 - 1578
Ruler of Echigo province and Kanto Kanrei
Uesugi Kenshin
1530 - 1578
Ruler of Echigo province and Kanto Kanrei
 Enomoto Takeaki
1836 - 1908
Naval officer and statesman
Enomoto Takeaki
1836 - 1908
Naval officer and statesman
 Taishi Shotoku
574 - 622
Regent, politician, and author
Taishi Shotoku
574 - 622
Regent, politician, and author
 Konosuke Matsushita
1894 - 1989
Founder of Panasonic
Konosuke Matsushita
1894 - 1989
Founder of Panasonic
 Hideto Matsumoto
1964 - 1998
Lead guitarist of X Japan and solo artist
Hideto Matsumoto
1964 - 1998
Lead guitarist of X Japan and solo artist
 Osamu Dazai
1909 - 1948
Novelist, short story writer
Osamu Dazai
1909 - 1948
Novelist, short story writer
 Shoya Tomizawa
1990 - 2010
Moto2 rider
Shoya Tomizawa
1990 - 2010
Moto2 rider
 Inukai Tsuyoshi
1855 - 1932
Prime Minister of Japan
Inukai Tsuyoshi
1855 - 1932
Prime Minister of Japan
 Kon Ichikawa
1915 - 2008
Film director and screenwriter
Kon Ichikawa
1915 - 2008
Film director and screenwriter
 Nakano Takeko
1847 - 1868
Leader of the Jōshitai (Girls' Army)
Nakano Takeko
1847 - 1868
Leader of the Jōshitai (Girls' Army)
 Eiji Toyoda
1913 - 2013
President and chairman of Toyota Motor Corporation
Eiji Toyoda
1913 - 2013
President and chairman of Toyota Motor Corporation
 Shintaro Katsu
1931 - 1997
Zatoichi, the blind swordsman
Shintaro Katsu
1931 - 1997
Zatoichi, the blind swordsman
 Tokugawa Hidetada
1579 - 1632
Second shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty
Tokugawa Hidetada
1579 - 1632
Second shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty
 Himiko
170 - 248
Ruler of Yamatai-koku
Himiko
170 - 248
Ruler of Yamatai-koku
 Isao Inokuma
1938 - 2001
Judo champion
Isao Inokuma
1938 - 2001
Judo champion
 Noboru Takeshita
1924 - 2000
Prime Minister of Japan
Noboru Takeshita
1924 - 2000
Prime Minister of Japan
 Emperor Nintoku
-290 - -399
16th Emperor of Japan
Emperor Nintoku
-290 - -399
16th Emperor of Japan
 Shigeo Shingo
1909 - 1990
Industrial engineer and consultant
Shigeo Shingo
1909 - 1990
Industrial engineer and consultant
 Shusaku Endo
1923 - 1996
Novelist and essayist
Shusaku Endo
1923 - 1996
Novelist and essayist
 Shinzo Abe
1954 - 2022
Prime minister of Japan
Shinzo Abe
1954 - 2022
Prime minister of Japan
 Tsuguharu Foujita
1886 - 1968
Painter and printmaker
Tsuguharu Foujita
1886 - 1968
Painter and printmaker
 Koji Wada
1974 - 2016
Singer of Digimon theme songs
Koji Wada
1974 - 2016
Singer of Digimon theme songs
 Saigo Takamori
1828 - 1877
Samurai, Meiji Restoration leader
Saigo Takamori
1828 - 1877
Samurai, Meiji Restoration leader
 Hayato Ikeda
1899 - 1965
Prime minister of Japan
Hayato Ikeda
1899 - 1965
Prime minister of Japan
 Mas Oyama
1923 - 1994
Karate master and founder of Kyokushin Karate
Mas Oyama
1923 - 1994
Karate master and founder of Kyokushin Karate
 Taira no Masakado
870 - 940
Provincial magnate and rebel leader
Taira no Masakado
870 - 940
Provincial magnate and rebel leader
We Need -- admin in