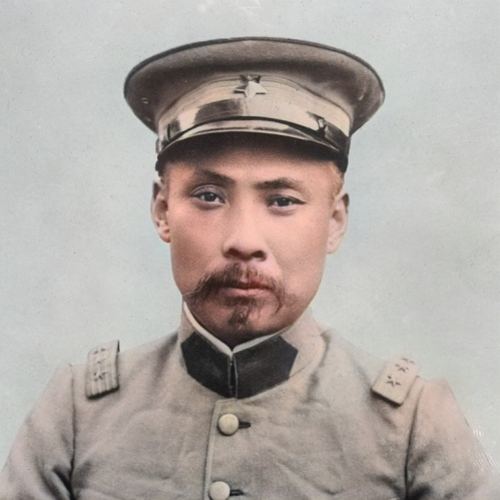
Personal
Other names:
Job / Known for:
President of the Republic of China
Left traces:
The Beiyang government and the warlord era
Born
Date:
1859-01-07
Location:
CN
Hejian, Hebei
Died
Date:
1919-12-12 (aged 60)
Resting place:
CN
Yuan Lin, Anyang, Henan
Death Cause:
Uremia
Family
Spouse:
Yu Yishang, Lady Shen, Lady Lee, Lady Kim, Lady O, Lady Yang, Lady Ye, Lady Zhang, Lady Guo, Lady Liu
Children:
Yuan Keding, Yuan Kewen, 15 other sons, 15 daughters
Parent(s):
Li Chaoxiang, Madame Yang
QR Code:
Show More
Rank
Users ranking to :
Thanks, you rate star
Ranking
5.0
1
About me / Bio:
Show More
Article for Feng Guozhang
Died profile like Feng Guozhang
Comments: